- Types of cloud computing services
- 1. SaaS (Software as a Service)
- 2. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- 3. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- Cloud computing service providers
- 1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- 2. ServerSpace
- 3. Microsoft Azure
- 4. Google Cloud Platform
- 5. IBM Cloud Services
- 6. Adobe Creative Cloud
Cloud computing has emerged as the optimal method of delivering enterprise software for businesses introducing new technologies or expanding their infrastructure. Many new technologies now begin in the cloud as services, which is very enticing to business customers who are aware of the possible competitive benefits of early adoption.
What is cloud computing?
Nowadays, it appears like everything is taking place “in the cloud.” But what is cloud computing?
The quick response is that it’s located somewhere at the other end of your internet connection; it’s a location from which you may access apps and services and where your data can be safely stored.
To put it simply, cloud computing makes it possible to rent your IT rather than buy it. Instead of making substantial investments in databases, software, and hardware, businesses prefer to access their computing power over the internet or in the cloud. They pay for it as they need it. Just a few of the existing cloud services include servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and business intelligence.
Cloud computing definition
The term “cloud computing” refers to an abstraction of computation, storage, and network infrastructure that has been put together as a platform for the rapid deployment and flexible scaling of systems and applications.
Self-service is essential to cloud computing since it allows users to get started right away by just filling out a web form. The speed, scalability, and flexibility that cloud computing offers enable firms to create, innovate, and support corporate IT solutions.
Cloud computing - How does it work?
Cloud storage functions by allowing users to access and download data on any selected device, such as a laptop, tablet, or smartphone, via an Internet service connection. Users of cloud storage can interact with other users to edit documents at the same time, making working remotely more convenient. The cost of cloud storage varies depending on your needs. As an individual user, you can typically receive starter amounts of cloud storage for free. For example, Apple’s iCloud offers 5 GB for free, despite its history of publicly documented security problems. For more storage, you must pay a price. Depending on the services you use, monthly or yearly prices are typical pricing structures.
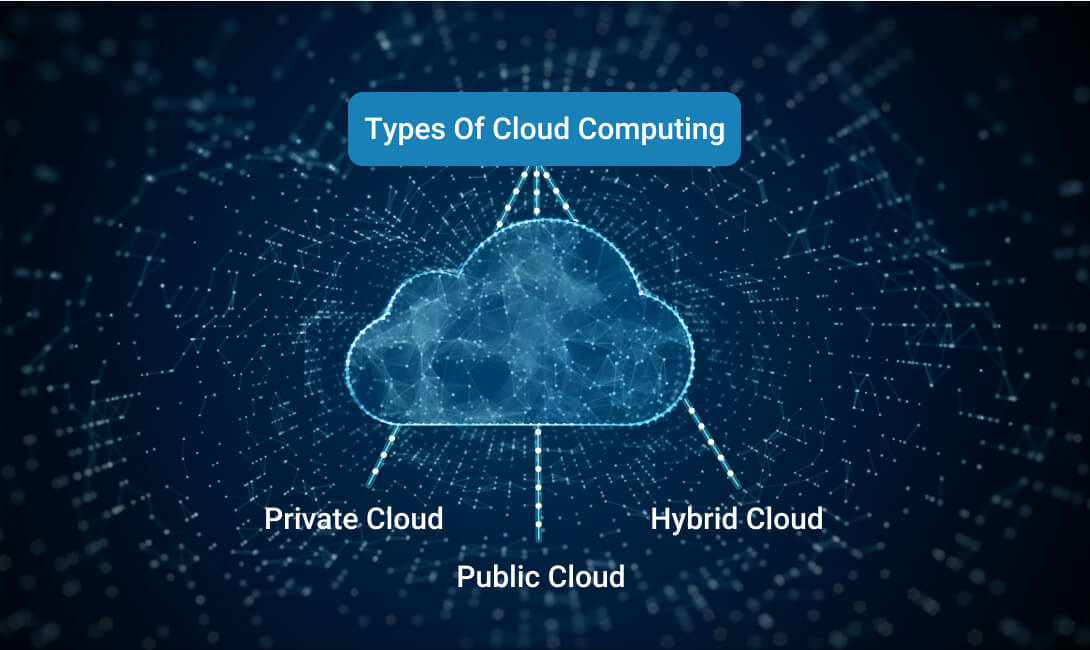
Types of cloud computing
Cloud computing is a topic that can easily become complicated when people discuss it. One of the main causes of this is the many types of cloud computing services available. Each of these has unique capabilities. The following three types of cloud computing are:
1. Public cloud
The public cloud can be defined as a huge collection of instantly accessible computing resources, including networking, memory, central processing units (CPUs), and storage. You can rent these resources to create an IT infrastructure because they are hosted in one of the public cloud vendors’ internationally dispersed and well-managed data centres. If you don’t want the headache of setting up and administering the entire solution, you can rent managed services. Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Microsoft Azure are the top suppliers of this kind of cloud service, although there are others.
2. Private cloud
The private cloud is only used by one company. It could be hosted on-site by the company or in the data centre of the cloud service provider. The maximum level of protection and control is offered by a private cloud.
A private cloud combines IaaS and public cloud operating technologies into software that can be installed and run in a customer’s data centre. Internal clients can supply their virtual resources to develop, test, and execute applications, just like in a public cloud, with metering to bill departments for resource use. The private cloud reduces the need for human provisioning and management, making it the pinnacle of data centre automation from an administrator’s perspective.
3. Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud combines both public and private clouds, as the name implies. For more protection and control, hybrid cloud customers typically host their business-critical apps on their servers while storing their non-critical applications at the cloud provider’s facility.
When hybrid cloud technology is at its most advanced, it entails building parallel environments that enable seamless application switching between private and public clouds. In other cases, databases may remain in the customer’s data centre and interface with public cloud applications; alternatively, during periods of high demand, virtualized data centre workloads may be duplicated to the cloud. Although private and public cloud integrations can take many different forms, they must be thorough in order to qualify as hybrid clouds.
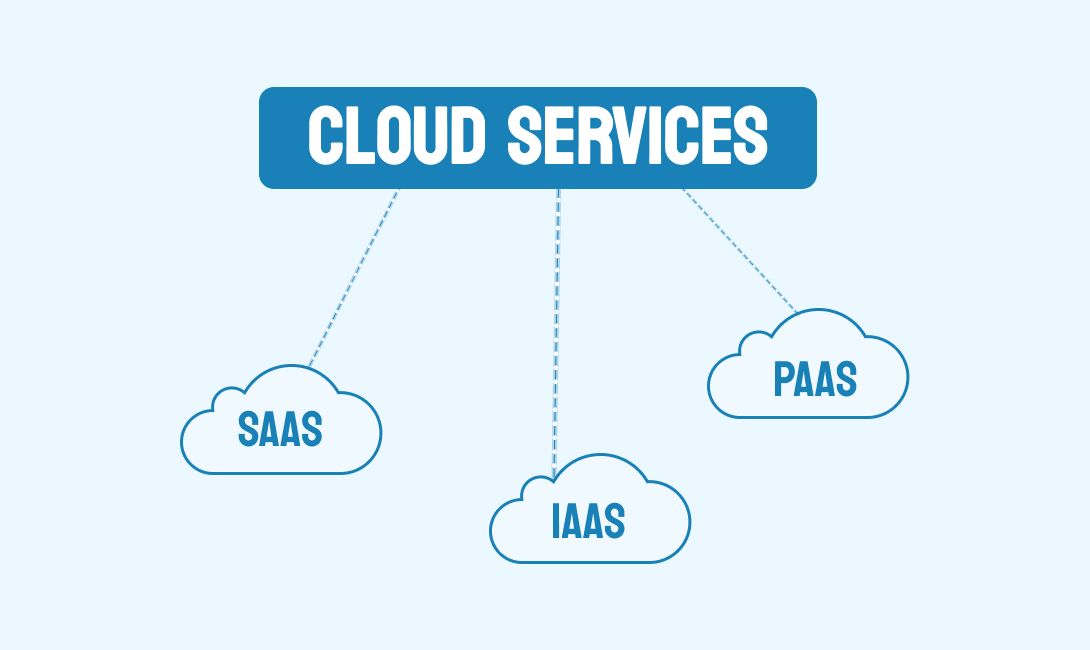
Types of cloud computing services
Your selection of a cloud computing service model will depend on how much control, adaptability, and management your company needs. Cloud computing is not a stand-alone piece of technology, like a chip or a phone. Instead, it is a system made up mostly of three primary types of cloud computing service models: SaaS (software-as-a-service), IaaS (infrastructure-as-a-service), and PaaS (platform-as-a-service).
1. SaaS (Software as a Service)
Software as a Service (SaaS) offers the entire application stack, from the supporting infrastructure to upkeep and upgrades for the app software, as a service. A SaaS solution is typically an end-user application where the cloud service provider manages and maintains both the infrastructure and the service.
Applications are delivered across the internet using this kind of cloud computing, often with a browser-based user interface. Most software firms today offer their products through SaaS, if not exclusively, at least as an option.
The most popular SaaS business applications are found in Google’s G Suite and Microsoft’s Office 365. SaaS apps frequently provide a wide range of configuration choices as well as development environments that let users contribute and modify their code. They also make it possible for on-premises apps to integrate data.
2. IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
Access to IT infrastructure services like computation, storage, networking, and virtualization is provided via infrastructure as a service (IaaS). You can control your IT resources most easily with this method, and it is similar to conventional on-premises IT resources.
Customers can use IaaS to get infrastructure services online and as needed. The main advantage is that the cloud provider manages the infrastructure that provides subscribers with computation, storage, and network capacity. This allows them to run their applications in the cloud. DevOps engineers develop, operate, manage, and deliver cloud-based applications and services, as well as the infrastructure supporting them. Any software on cloud-native solutions, including database, middleware, and application software, must typically be installed, configured, secured, and maintained by the cloud subscriber.
Imagine it as a data centre that is remotely managed by a third party. However, with a software layer that virtualizes all of those resources and streamlines customers’ ability to assign them. The first IaaS provider was and is still Amazon Web Services, which is followed by Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, Alibaba Cloud, and IBM Cloud.
Each organisation chooses its own method for managing its cloud infrastructure. Some opt for Cloud Management Services that can handle a broader mission with a clear focus on managing hybrid environments and resources. Some businesses handle it themselves, while others hire a cloud MSP to relieve the immediate stress.
3. PaaS (Platform as a Service)
All the hardware and software resources required for the creation of cloud applications are provided via the platform as a service (PaaS). With PaaS, businesses can completely concentrate on developing applications without having to worry about managing and maintaining the supporting infrastructure.
Developers that use shared tools, procedures, and APIs can speed up the development, testing, and installation of apps using PaaS’s workflows and service sets. PaaS for businesses can guarantee that developers have immediate access to resources, adhere to particular procedures, and only access a limited set of services. Operators look after the underlying infrastructure.
PaaS solutions must include readily available programming components that let programmers add new functionality to their apps, including cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), chatbots, blockchain, and the Internet of Things (IoT). The ideal PaaS solution should also offer big data analytics, content management, database administration, systems management, and security for analysts, end users, and professional IT administrators.
What is the purpose of cloud computing?
The majority of people utilise the cloud without even realising it because it has become so ingrained in our daily lives. Life without the cloud would be drastically different for many people. Facebook, Spotify, Gmail, and Twitter wouldn’t exist.
The corporate landscape has also changed as a result of the cloud. Cloud services are now used by millions of businesses worldwide for everything from document generation and backup to social CRM and accounts.
This is how it appears:
- Approximately 545 cloud applications or services are used by companies with more than 25,000 employees.
- There were 2.09 billion daily active Facebook users globally as of July 2022.
- Cloud-based email services like Gmail and Yahoo! Mail are used by more than half of all Internet users to send and receive messages.
Larger companies can also save a lot of money this way. Prior to the cloud, companies invested in costly information management infrastructure, technology, development, and maintenance. Businesses can replace expensive web servers and IT staff with fast Internet connections, allowing workers to do jobs online.
You can hire a cloud architect to assist you in creating the architecture, which includes application development, data management, and identity and access management, among other IT-related domains. The architect’s job is to make sure that all of these components function harmoniously.
Cloud computing examples
1. Examples of cloud storage: Dropbox, Gmail, Facebook
2. Examples of marketing cloud platforms: Salesforce, Hubspot, Adobe Marketing Cloud
3. Examples of cloud computing in education: SlideRocket, Ratatype, Amazon Web Services
4. Examples of cloud computing in healthcare: ClearData, IBM Cloud, Dell’s Secure Healthcare Cloud
5. Examples of cloud computing for government: IT consolidation, Shared services, Citizen services
Cloud computing service providers
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is the most secure cloud platform available, providing a variety of infrastructure services like database storage, processing power, and networking. One can host static websites with this AWS. Users can create complex applications that are reliable, scalable, and flexible by utilising such services. It also provides free access to hands-on AWS training.
2. ServerSpace
The cutting-edge hyper-converged vStack platform used by Serverspace Cloud is built on top-notch open-source technology. The development of next-generation virtual machines is aided by the FreeBSD operating system and the lightweight Bhyve hypervisor. The servers are guaranteed to be reliable at 99.9% SLA or you’ll get a refund of your money. Experience the high-end servers’ performance with ServerSpace.
3. Microsoft Azure
Through a global network, applications are deployed, designed, and managed using Microsoft Azure. Windows Azure was the previous name for Microsoft Azure. This cloud computing service supports a wide range of operating systems, databases, tools, programming languages, and frameworks. For 30 days, Microsoft Azure is accessible as a free trial.
4. Google Cloud Platform
The Google Cloud Platform makes use of resources from Google data centres, including computers, virtual machines, hard drives, etc. Developers and businesses utilise the Google Cloud Platform as an integrated storage system for real-time data. In addition to the free trial, this service is accessible through a number of convenient Pay-As-You-Go payment plans (PAYG).
5. IBM Cloud Services
Iaas, PaaS, and SaaS are all available through the IBM Cloud’s various cloud delivery models. When planning or developing your next-generation services or apps, you can freely combine the tools, data models, and delivery methods of your choice using IBM Cloud. Building ground-breaking solutions that add value to your organisations and industry uses IBM Cloud. You may integrate high-performing cloud communications and services into your IT environment using the IBM Bluemix Cloud platform.
6. Adobe Creative Cloud
There are various products from Adobe that offer cloud services. Adobe Creative Cloud, Adobe Experience Cloud, and Adobe Document Cloud are just a few of them. The Adobe Creative Cloud service is a software-as-a-service that allows customers to use Adobe tools for editing films, taking photos, and creating graphics. Users of the Adobe Experience Cloud have access to a wide range of tools for creating campaigns, advertising, and gathering business intelligence. A complete solution for digital documents is Adobe Document Cloud.
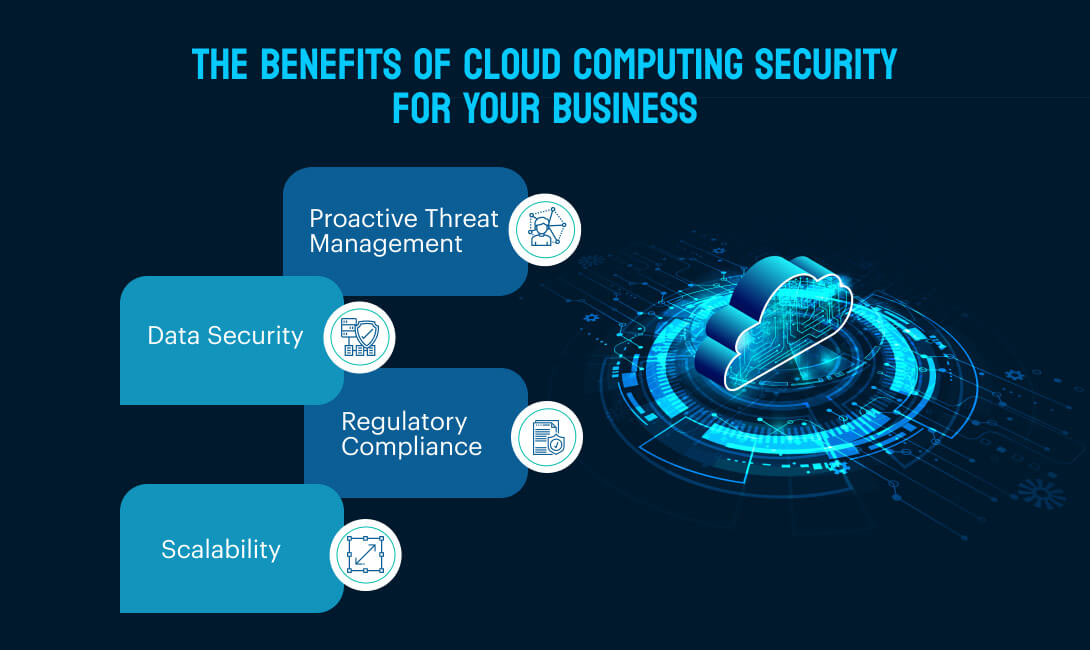
The benefits of cloud computing security for your business
Proactive threat management
Cloud computing security can identify attacks more quickly by utilising end-point scanning and global threat intelligence. This aids in determining the threats to the organisation’s mission-critical assets in relation to the threat environment.
Data security
The best cloud computing security solutions include data security by default. To stop unwanted entities from obtaining private data, they have security methods and policies in place, such as strict access controls and data encryption.
Regulatory compliance
Excellent cloud application security providers support compliance with statutory mandates and industry-specific standards. This is achieved through managed security services, as well as an upgraded infrastructure.
Scalability
In reaction to variations in demand, a scalable cloud computing solution can adjust capacity, security coverage, and pricing. To prevent server crashes, for instance, server capacity is increased during times of high demand. Charges are reduced regardless of decreased demand. Why spend money on more infrastructure when fluctuating demand can result in the underutilization of expensive equipment?
High availability and support
Cloud computing security solutions usually contain redundancies to ensure that the application and its resources are always available. The CDNs in use feature distributed, global networks of edge servers that facilitate effective content delivery, boost application performance, and limit server access. They handle traffic peaks better than on-premises/hardware solutions.
Conclusion
Business owners and other key stakeholders ought to consider replacing their outdated, physical IT infrastructure with a more flexible and agile alternative like the cloud. Your business will change for the better in many ways when switching to a cloud computing solution. In general, cloud computing is used for applications that store and process large amounts of data quickly, and require more storage and processing power than most businesses can afford.
For greater storage options, scalability, and other services that the cloud offers, the majority of organisations and corporations are figuring out how to move to the cloud. Despite all of this, many businesses are just beginning their journeys into the cloud, and the potential for using cloud services in the future is seemingly unlimited.
COMMENT
No Comments found.
DETAILED INDUSTRY GUIDES
Software Development - Step by step guide for 2021 and
beyond | OpenXcell
Learn everything about Software Development, its types, methodologies, process outsourcing with our complete guide to software development.
Headless CMS - The complete guide for 2021 | OpenXcell
Learn everything about Headless CMS along with CMS, its types, pros & cons as well as use cases, and real-life examples in a complete guide.
Mobile App Development - Step by step guide for 2021 and beyond | OpenXcell
Building your perfect app requires planning and effort. This guide is a compilation of best mobile app development resources across the web.
DevOps - A complete roadmap for software transformation | OpenXcell
What is DevOps? A combination of cultural philosophy, practices, and tools that integrate and automate between software development and the IT operations team.
GET QUOTE
INSIGHTS INTO TECH
The inception of ChatGPT in 2022 marked the wide-scale adoption of Artificial Intelligence in application development. In the field of creating mobile apps, AI-powered tools and frameworks have become indispensable…
Read more...
Introduction Most industries have turned to AI to stay ahead of the competition in the evolving tech landscape. The construction industry is no stranger to this trend. The advent of…
Read more...
Introduction Digital transformation needs no introduction; it is evolving as a norm in many industries. The paradigm transition it brings to the retail landscape is evident from the latest predictions.…
Read more...