Most elements of our personal and professional lives are governed by contracts, which are crucial for modern society to function. Smart contracts are a key component of blockchain technology since they make transactions more organised and safe. Furthermore, it makes other elements, such as applications running on these platforms, even more accessible. Let’s first understand what a smart contract actually is.
What is Smart Contract?
A smart contract, also known as a “crypto contract,” is a computer programme that, under certain conditions, directly and automatically regulates the transfer of digital assets between parties. Similar to a traditional contract, a smart contract operates with automatic contract enforcement. Smart contracts are computer programmes that run exactly as their developers have coded or programmed them to. Smart contracts are enforceable by code, just like a traditional contract is by law.
In response to the fulfilment of specific requirements, smart contracts are computer programmes or protocols for automatic transactions that are kept on a blockchain. In other words, smart contracts automate the execution of contracts so that all participants may quickly determine the result without the need for a middleman or a waiting period.
According to American computer scientist Nick Szabo, smart contracts are computerised transaction protocols that carry out contract terms. Szabo created the virtual currency “Bit Gold” in 1998. Its application makes transactions transparent, irreversible, and traceable.
Smart Contracts definition
Like any other contract, a smart contract specifies the conditions of an agreement. However, in contrast to a traditional contract, the rules of a smart contract are carried out as code that runs on a blockchain like Ethereum. Smart contracts enable developers to integrate peer-to-peer functionality into their apps, leveraging the security, dependability, and accessibility of the blockchain across finance, insurance, logistics, gaming, and many other industries.
How do Smart Contracts work?
Putting “if/when…then” logic into code and placing it on a blockchain is how smart contracts work. When predefined circumstances have been verified to have been met, a network of computers will carry out the actions. These can include paying money to the right people, registering a car, sending out notifications, or issuing a ticket. When the transaction is finished, the blockchain is updated thereafter. As a result, the transaction cannot be modified, and only parties to whom permission has been granted can access the outcome.
Smart contracts can include as many conditions as necessary to reassure participants that the activity will be successful. To set the terms of the blockchain, participants must determine how transactions and their data will be represented. Agree upon the “if/when…then…” rules that govern those transactions, think through any potential exceptions, and create a framework for resolving disputes.
The smart contract can then be created by a developer. However, more and more businesses using blockchain for business are offering templates, web interfaces, and other online tools to make smart contract architecture simpler.
Let’s look at a few examples of smart contracts to understand how they work.
- The amount (in cryptocurrency) will be transferred to you ONLY IF you send object A.
- This “A” object will be given to you ONLY IF you send a specific amount of digital assets (cryptocurrencies such as ether or bitcoin).
- The digital materials indicated in the contract will be sent to me ONLY IF I complete the work.
The most popular Smart Contract platforms
- Ethereum smart contracts
- Bitcoin smart contracts
- Solana smart contracts
- Hyperledger fabric smart contracts
- Stellar smart contracts
Industrial applications of Smart Contracts
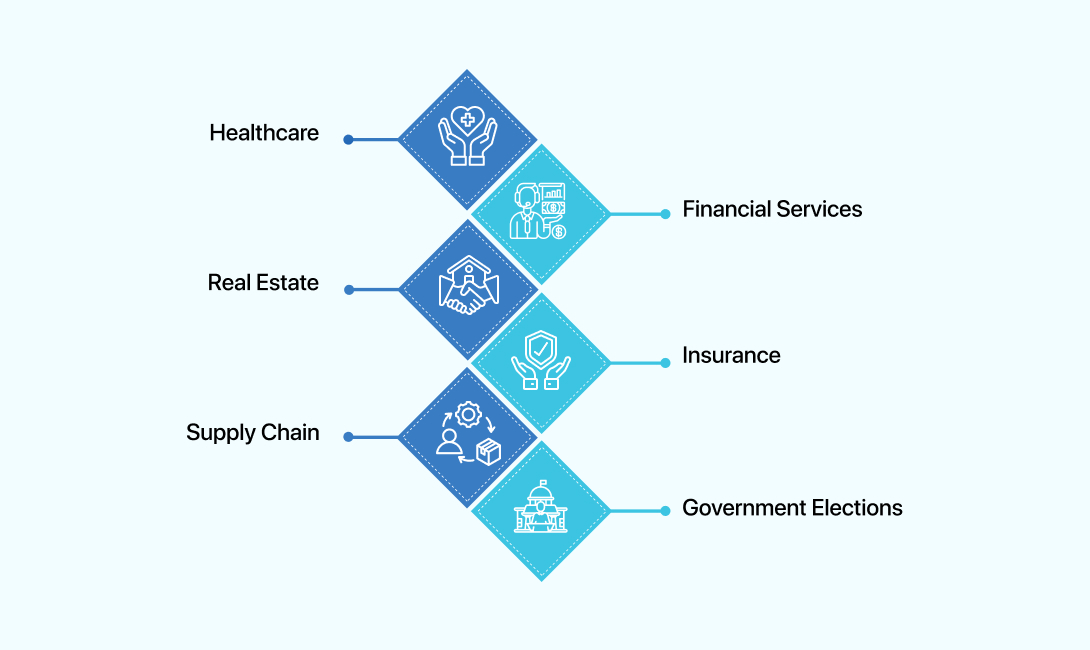
Smart contracts have several possible applications that could automate the world and make it simpler to live in. Explore how different businesses can benefit from smart contract development in active blockchain solutions.
1. Healthcare
With the use of a private key, the blockchain can store patients’ encoded medical records. For reasons of privacy, only selected people would be given access to the records. In the same way, smart contracts allow for private and secure data storage.
Blockchain can be used to store all patient hospital receipts and automatically share them with insurance providers as proof of care. The ledger can also be used for a variety of tasks, including managing supplies, monitoring medications, and adhering to regulations.
2. Financial services
Smart contracts play a major role in transforming traditional financial services. Insurance claims are handled through error checking, routing, and, if everything is deemed proper, money can be easily transferred to the user.
Smart contracts integrate essential bookkeeping capabilities and eliminate the possibility of accounting records being compromised. Additionally, they make it possible for shareholders to participate transparently in decision-making. They also help in trade clearing, which is the process of transferring money after trade settlement amounts have been determined.
3. Real estate
Brokers play an important role in the traditional real estate market. Owners will engage a broker to take care of the challenging portions for them, such as paperwork and finding a buyer. Given that, selling a house is nothing sort of a lengthy and complicated process. However, that seems perfect for the seller because brokers charge a hefty commission on the sale price of the home.
In order to streamline the house-transfer procedure while maintaining the same level of security as with an intermediary, a smart contract can be used in place of a broker.
4. Insurance
Smart contracts could be advantageous for insurance coverage. In essence, when a user enrolls in a policy, they enter into a smart contract with the provider. The smart contract, which the user would read and sign if they agreed, would contain all policy criteria.
Until the responsible party requires it, the contract will remain in effect. After uploading the necessary documents demonstrating their necessity for the insurance payment, the cash would then be made available. This kind of agreement eliminates the requirement for communication with insurance companies and people.
5. Supply chain
Supply chains typically suffer from paper-based systems where forms must go through several channels to receive clearance. Fraud and loss are more likely to occur as a result of the tedious process.
By providing parties involved in the chain with an accessible and secure digital version, blockchain can eliminate these concerns. Inventory control, payment automation, and task automation are all possible with smart contracts.
6. Government elections
It would be very difficult to decode the voter address and change the vote once it has been entered into the blockchain, increasing confidence in unethical acts.
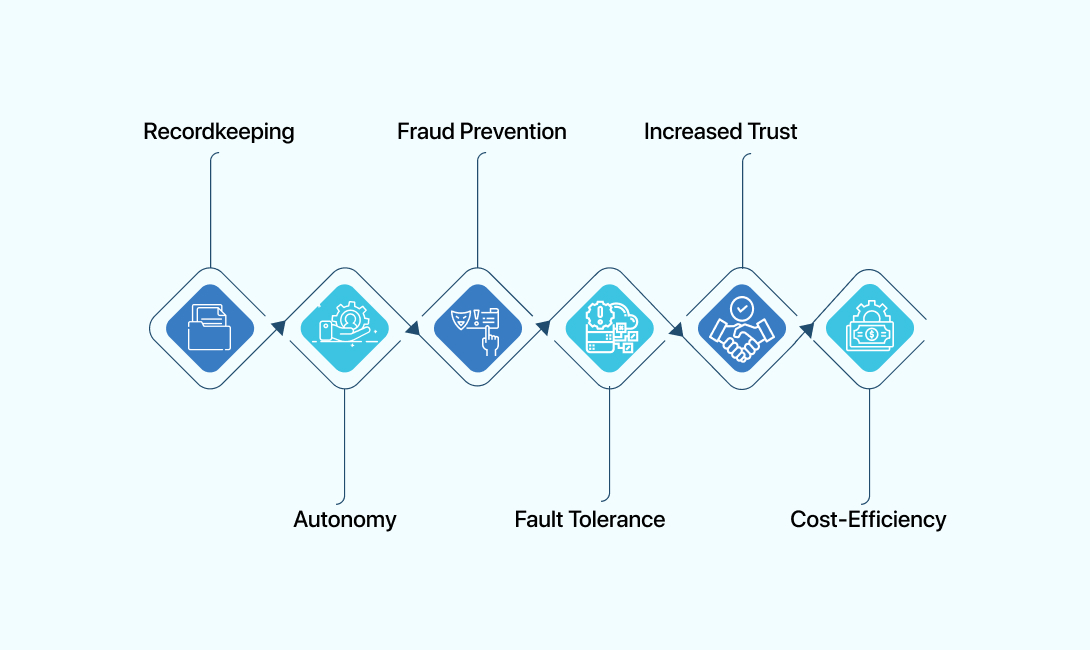
Benefits of Smart Contracts
1. Recordkeeping
The blockchain records all contract transactions in chronological order and makes them accessible, along with a full audit trail. To provide complete privacy, the parties involved can be safeguarded cryptographically.
2. Autonomy
The parties engage in direct communication. Smart contracts do away with the need for middlemen and enable open, direct communication with customers.
3. Fraud prevention
Businesses can benefit from identifying and controlling fraudulent activities. Smart contracts are stored on the blockchain. It is extremely difficult to forcefully alter the blockchain since it requires a lot of computation. A smart contract breach can also be discovered by network nodes, and in that case, the attempt is flagged as invalid and not recorded in the blockchain.
4. Fault tolerance
Because no single person or organisation controls digital assets, one-party dominance and situations in which one party drops out do not occur. Additionally, because the platform is decentralised, the contract is still in place even if one node disengages from the network.
5. Increased trust
Contracts are automatically carried out and upheld. These agreements are also unchangeable, unbreakable, and undeniable since they are immutable.
6. Cost-efficiency
The use of smart contracts reduces expenses by doing away with the necessity for middlemen (brokers, attorneys, notaries, witnesses, etc.). It eliminates paperwork resulting in saving money and producing less waste.
The future of Smart Contracts
Unquestionably, smart requirements-powered contracts are the way of the future for relatively simple contracts that can be written and executed automatically whenever basic requirements are satisfied, like in residential conveyancing, where completion funds can be disbursed as soon as contracts are signed.
Different smart contract platforms will revolutionise how companies engage with their customers and in the supply chain while also saving them time and money around the world. Minimal human intervention will thereby liberate people and key decision-makers from dealing with tedious administration and red tape, allowing them to concentrate on their day jobs. It is a result of smart contracts taking up the slack.
Numerous banks and insurance companies already use smart contracts in their regular operations. Since they are already in use and being tested in actual situations, smart contracts will soon be a regular part of our daily activities. Despite the previous point, there is still going to be a long way to go before everything is controlled by a smart contract.
Looking for a reliable Blockchain Development Company? OpenXcell is a trusted blockchain development organisation offering effective Blockchain Development Services for small and established businesses.
COMMENT
No Comments found.
DETAILED INDUSTRY GUIDES
Software Development - Step by step guide for 2021 and
beyond | OpenXcell
Learn everything about Software Development, its types, methodologies, process outsourcing with our complete guide to software development.
Headless CMS - The complete guide for 2021 | OpenXcell
Learn everything about Headless CMS along with CMS, its types, pros & cons as well as use cases, and real-life examples in a complete guide.
Mobile App Development - Step by step guide for 2021 and beyond | OpenXcell
Building your perfect app requires planning and effort. This guide is a compilation of best mobile app development resources across the web.
DevOps - A complete roadmap for software transformation | OpenXcell
What is DevOps? A combination of cultural philosophy, practices, and tools that integrate and automate between software development and the IT operations team.
GET QUOTE
INSIGHTS INTO TECH
The inception of ChatGPT in 2022 marked the wide-scale adoption of Artificial Intelligence in application development. In the field of creating mobile apps, AI-powered tools and frameworks have become indispensable…
Read more...
Introduction Most industries have turned to AI to stay ahead of the competition in the evolving tech landscape. The construction industry is no stranger to this trend. The advent of…
Read more...
Introduction Digital transformation needs no introduction; it is evolving as a norm in many industries. The paradigm transition it brings to the retail landscape is evident from the latest predictions.…
Read more...